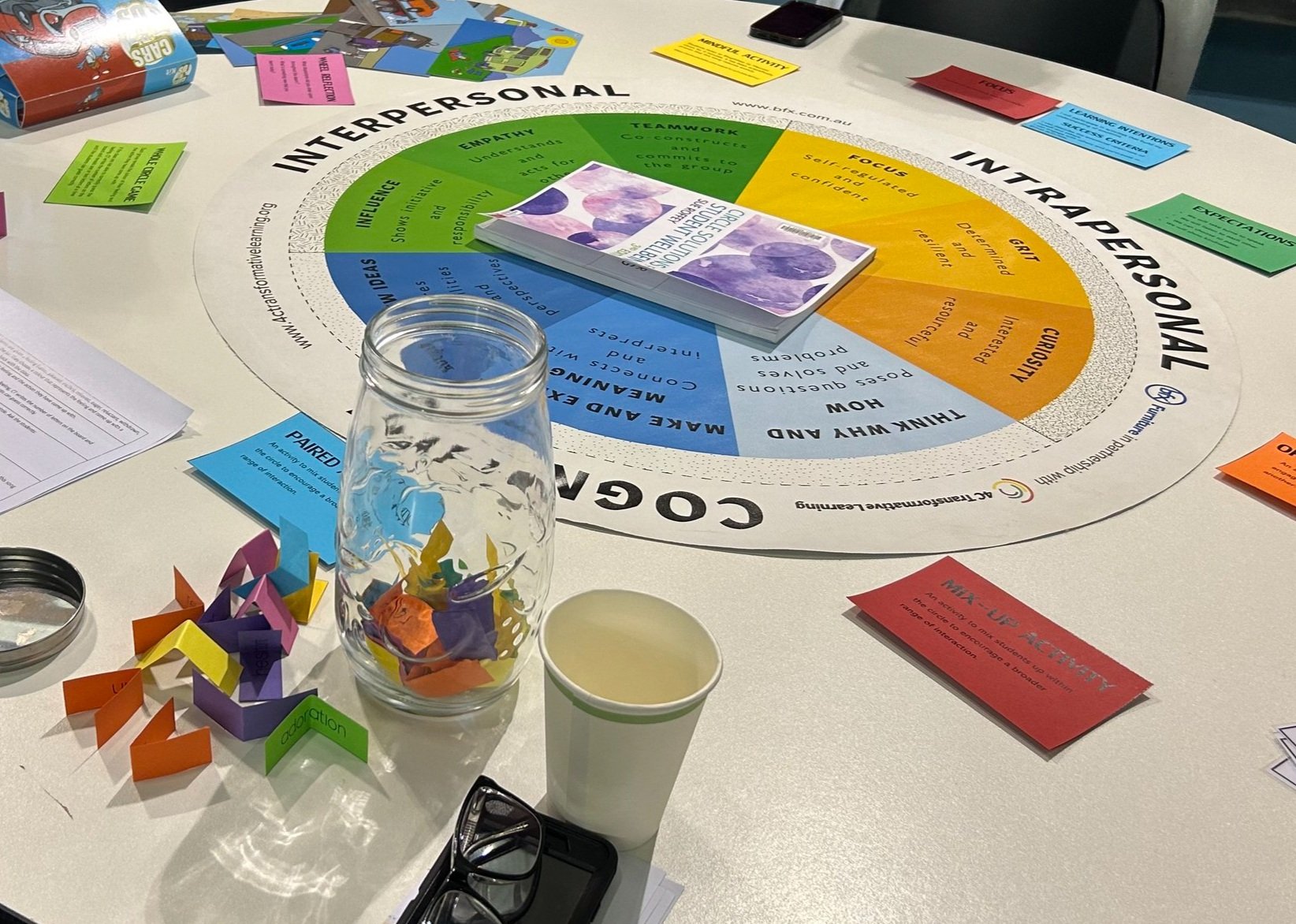
The 4CTL Learning Disposition Wheel
What is the Learning Disposition Wheel?
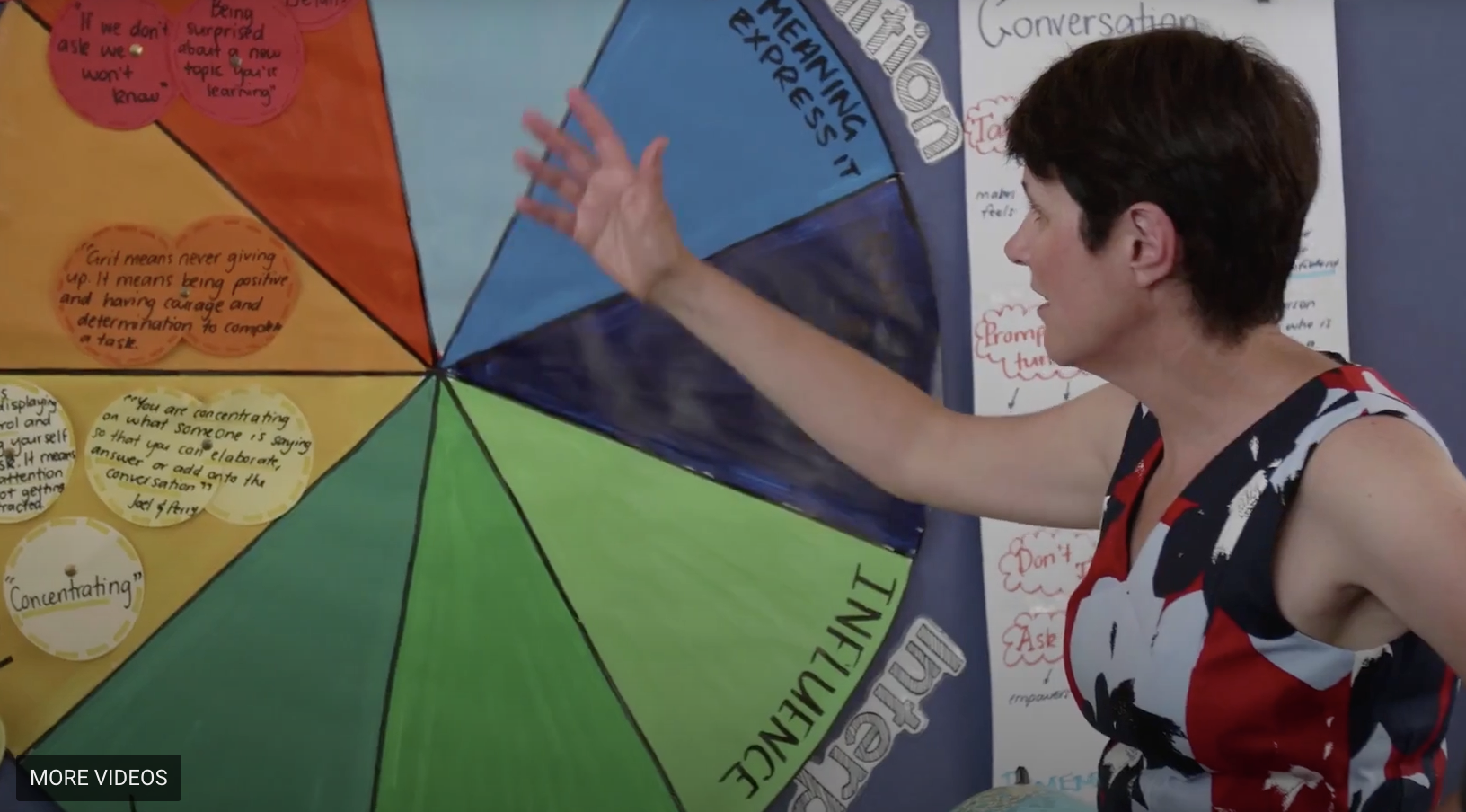
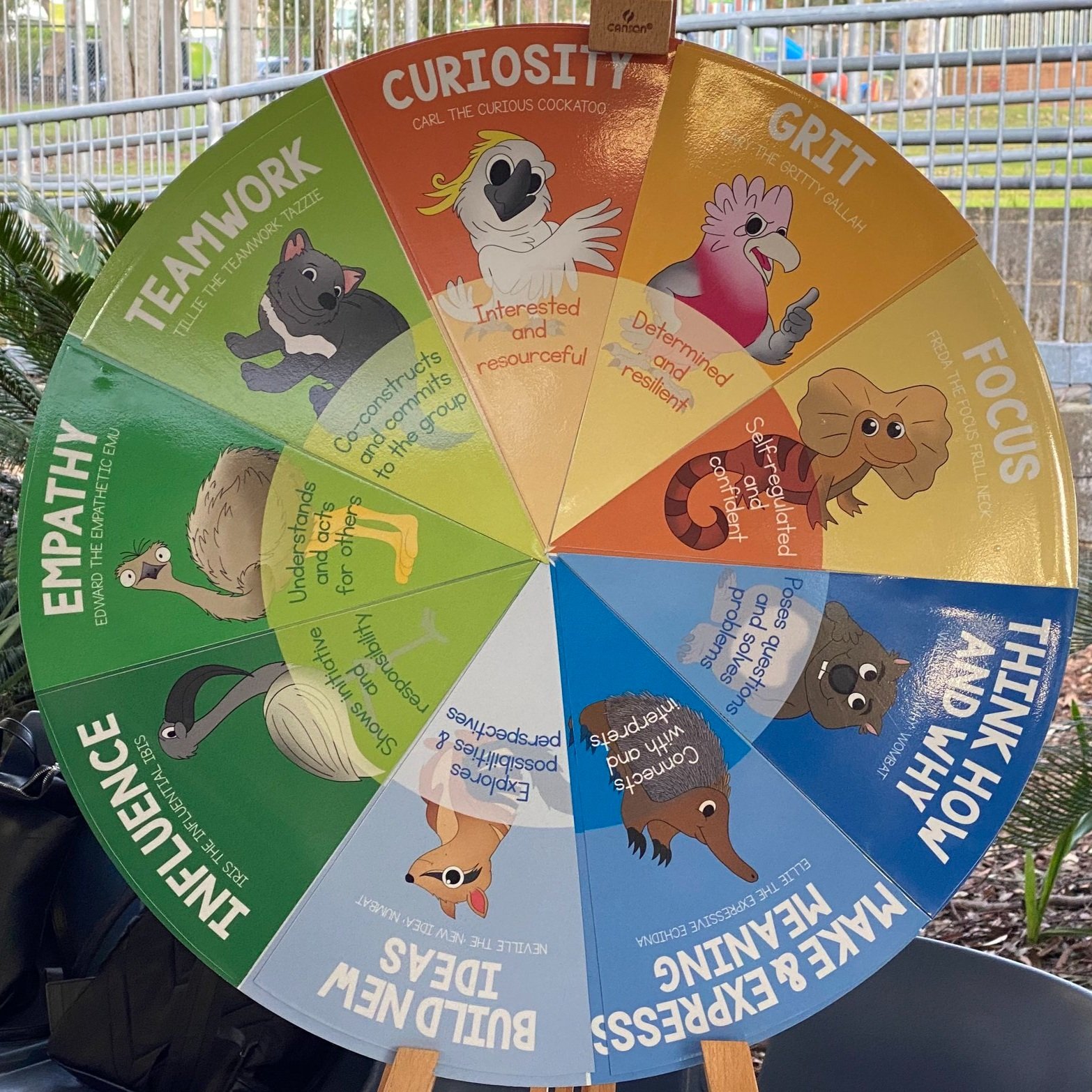
The Learning Disposition Wheel is a coherence maker or schema that identifies the dispositions needed for learners to develop a sense of agency and wellbeing. It is underpinned by the belief that learner capacity is not fixed, and that these essential capacities can be learnt when taught in the right way, both explicitly and implicitly.
The Wheel is used by many schools, early childhood centres, tertiary institutions and educational leaders as a tool to transform learning, pedagogy and learners, enabling deeper learning through its use as a diagnostic, feedback, reporting and evaluation tool through which teachers can deeply notice and analyse the strengths and yet-to-be strengths of learners. This then shapes pedagogy and curriculum learning design. The Wheel provides a common language across schools, organisations, and communities to talk about learning, learners, agency building, personal and collective challenges and much, much more.
The are the dispositions for learning?
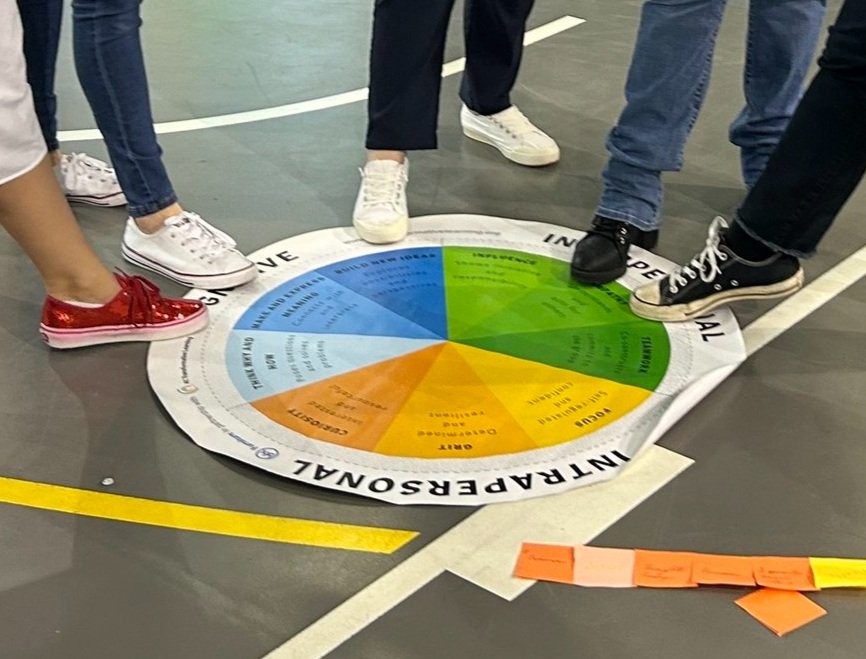
The nine dispositions are categorised into three domains - The Cognitive Dispositions (Think why and how; Make and express meaning; Build new ideas), The Interpersonal Dispositions (Influence; Empathy; Teamwork) and The Intrapersonal Dispositions (Focus; Grit; Curiosity).
How was the learning disposition wheel developed?
The National Research Council (NRC) 2012 report Education for Life and Work: Developing Transferable Knowledge and Skills in the 21st Century used a substantial research base to identify three broad domains for deeper learning capacity.
The three domains are:
The cognitive - the capacity to think and reason
The intrapersonal - the capacity of self-regulating emotions and behaviours to achieve goals
The interpersonal - the capacity to express, interpret and respond to messages from others.
The NRC report used a classification scheme to describe and align human competencies with these domains and argue that these competencies can be taught and learnt.
Research in Self-Determination Theory also informs our understanding of the Learning Disposition Wheel. This theory of motivation explains how competence, autonomy and relatedness are three basic psychological needs that support the development of agency, well-being and positive learning outcomes.
From this research, 4C Transformative Learning developed a metalanguage for the Wheel, in consultation with education leaders, teachers, students and parents.
How is the learning disposition wheel used in the classroom?
The Learning Disposition Wheel can be used to:
Design and engage in learning
When developing learning, the Wheel can guide teachers in explicitly teaching the dispositions. As students become more familiar with the dispositions, they are able to identify them in their learning and work to strengthen them, where they require development.
For instance, if a student is struggling and confused about a mathematical concept such as algebra, developing grit (determined and resilient) can assist her to persist through the difficulty and confusion, and develop strategies to navigate confusion.
This process of developing grit in facing difficulties can then be applied in other areas of learning, in and out of school.
Assess learning
In our partnership schools, we have co-developed assessment rubrics to use with each of the dispositions in the Wheel.
This means that schools who work with us are able to build assessment strategies and tasks that can show growth in the dispositions over time.
As a self-diagnosis tool for learning
In discussions about learning, students are often able to identify their strengths and their yet-to-be strengths on the wheel.
This self-diagnosis provides potential for deep critical reflection on how growth in the dispositions can be achieved, and can be a central tool for self-regulation and communication about learning struggles between students, teachers, parents and the wider school community.
How do teachers use the wheel?
Here is an extract from a discussion with Lucia, explaining how she uses the Learning Disposition Wheel:
“Through our initial navigation (mathematics) inquiry in line with the Learning Disposition Wheel, it became immediately apparent how the individual powers (competencies) of the Wheel were dependent on one another to deepen the learning.
The actual task required students to solve an open-ended problem, demonstrating a variety of measurement skills, incorporating geometry, fractions and decimals, and whole number understandings.
The complexities of the task immediately indicated that grit would be a targeted area from the Learning Disposition Wheel, if the students were to successfully complete the inquiry.
Through teacher observations during the beginning stages, it was identified that, even though students were enthusiastic and determined in their inquiry, teamwork was also an essential component. The learning experiences proved complex.
Scaffolded learning experiences quickly drew student attention to the need to plan the steps of their inquiry effectively, which could not be done individually, but as the result of working collaboratively with their team.
This led to the realisation that working effectively as a team meant each member had a responsibility to the team, and each was held accountable to complete the mini tasks, building on known understandings and skills.
During the course of their investigation, students learnt that the power of teamwork relied heavily on their ability to negotiate, listen to other points of view, challenge when necessary, and come to a consensus before moving forward.
This was highlighted when a team member who had been absent from school, when her team explained how they had solved the problem, challenged their solution, as they had not read all the information provided.
She demonstrated and proved her reasoning to her team.
Discussion of the roles, and responsibility, of each team member to double-check solutions and challenge each other’s ideas if they did not agree, rather than just accepting everything one or two teammates said, was a turning point for students, allowing them to make the connection between teamwork and grit.
Another connection to the Learning Disposition Wheel that became evident to the students was grit and think why and how.
Throughout the course of the inquiry, students had to constantly check for accuracy in their measurements, and select and apply appropriate strategies to solve problems.
There were numerous occasions that the students failed in their initial solutions, but due to teamwork, which fostered grit, the students encouraged one another and challenged where necessary, extending each other’s thinking and understanding, delving further into the learning by continually questioning, making decisions based on task requirements, proving their theories, and reflecting on their learning at each stage of the inquiry.
The connection between the powers of the Learning Disposition Wheel to student learning made the learning more authentic and powerful.”
What is the connection between the 4Cs and the Learning Disposition Wheel?
We believe the 4Cs overarch and underpin all learning and, as such, they are present in how each of us explore, embody and demonstrate the dispositions. The 4Cs are also embedded in many of the dispositions, as the following examples demonstrate:
Creativity is found in Build New Ideas (Cognitive Domain)
Critical Reflection is found in Think Why and How (Cognitive Domain)
Collaboration is found in Teamwork (Interpersonal Domain) and
Communication is found in Make and Express Meaning (Cognitive Domain).
We have written much more about the 4Cs and their relationship to the Learning Disposition Wheel in Transforming Schools,: Creativity, Critical Reflection, Communication and Collaboration.
More examples of the use of the Learning Disposition Wheel in schools
KOGARAH PS
Teachers, Students and Parents Learn to Use the Disposition Wheel to Help Self-Regulate Challenging Behaviour
Teachers at Kogarah Public School use the learning dispositions to help students and parents understand learning strengths and not-yet-strengths, and how to address the behaviour that arises when not-yet-strengths are activated. Read more here.
Kurri Kurri HS
Student Agency Using the Learning Disposition Wheel Improves Student Self Regulation
Kurri Kurri HS students struggling with self regulation while learning are guided through a dispositions-based self assessment. Students develop the language and meta-cognition to grow their dispositions, recognise when they’re struggling and ask for the help they need. Read more here.
I would like to explore the Learning Disposition Wheel, what can I do?
4C Transformative Learning work with early childhood, school and tertiary institutions in long term partnerships to transform learning, pedagogy, curriculum and leadership. Many of our partner schools choose to focus on developing the teaching, and learning, of dispositions from the wheel, which is possible with students of all ages, whether pre-school, primary, secondary or adult.
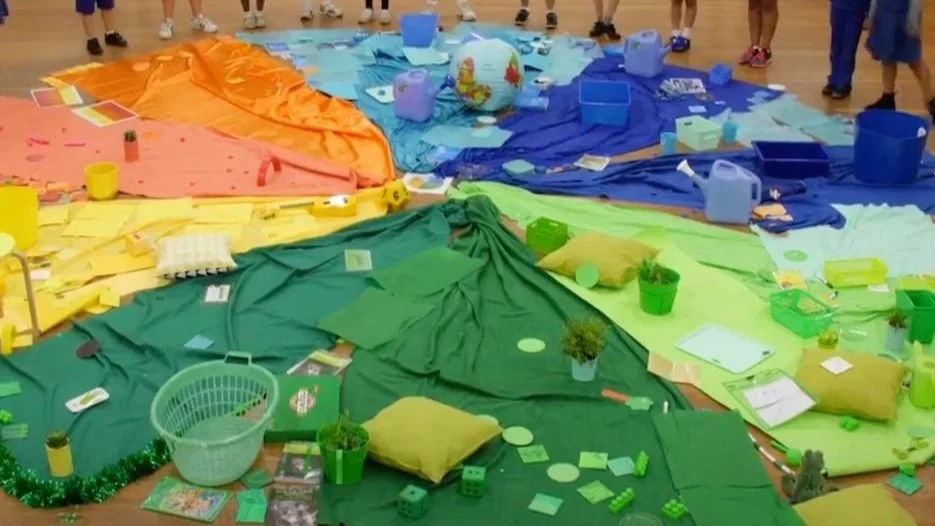
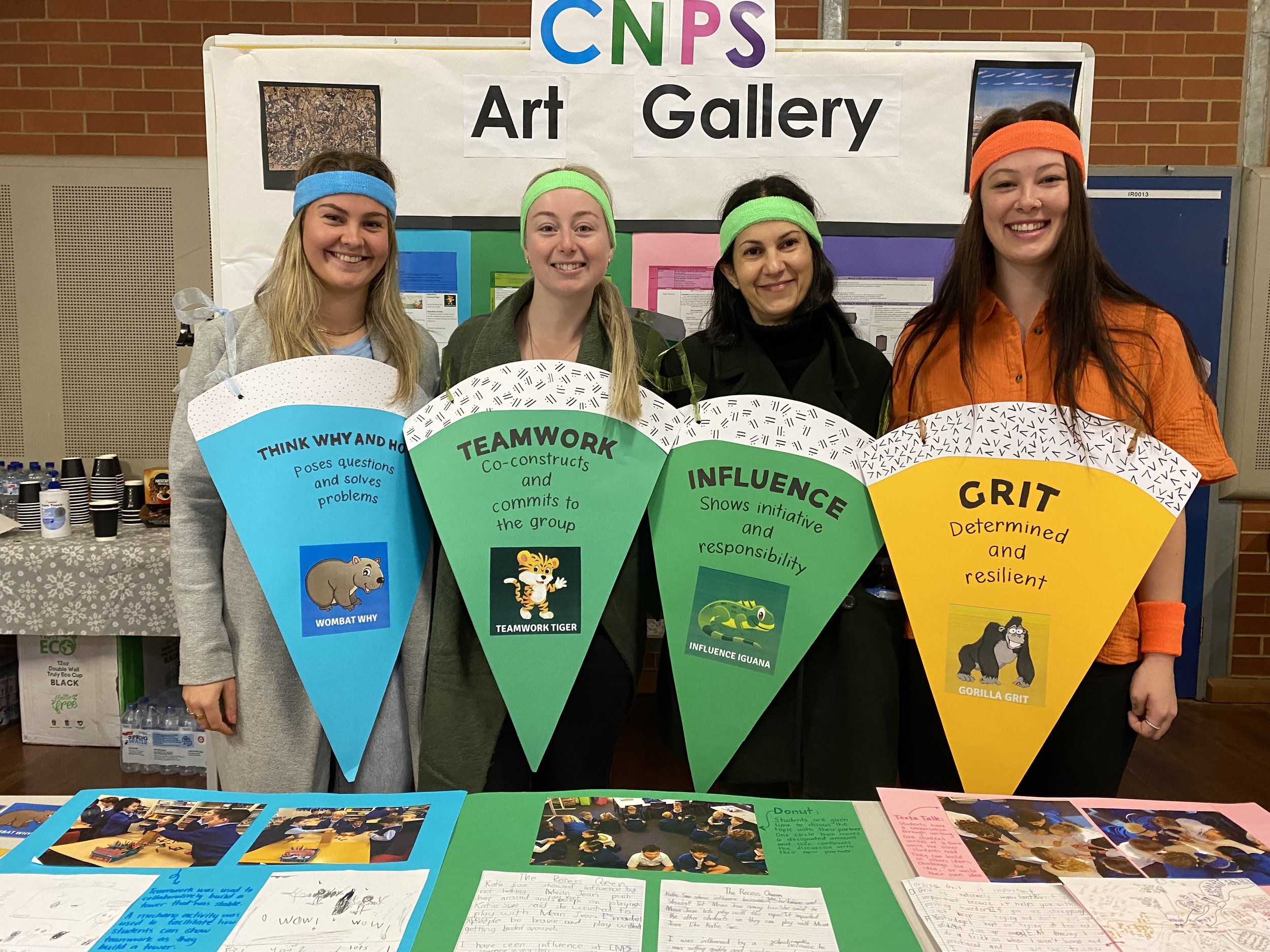
Along with the above examples, you can see images of the work of some of our schools, using the wheel with a variety of student ages, demographics and locations, as well as images of working with the wheel in teacher and leaderships groups.
If you would like to discuss professional learning based on the Learning Disposition Wheel, the 4Cs, or anything in our curriculum, please contact us via our contact form.
Our co-founders, Miranda Jefferson and Michael Anderson, have two books that unpack the Learning Disposition Wheel further. Transforming Schools introduces the wheel and Transforming Education explores the wheel in depth. Read more about these books here.
Vinyl Learning Disposition Wheels are available for purchase from us.